- info@ficci.org.bd
- |
- +880248814801, +880248814802
- Contact Us
- |
- Become a Member
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |

Bangladesh's journey to becoming a digital economy will not be defined only by smartphones or social media penetration. It will be determined by how deeply technology transforms its most powerful economic engine: the readymade garments (RMG) sector.
 As the world's second-largest apparel exporter, the RMG industry contributes 10.35% to the national GDP and generates nearly USD 47 billion in annual exports, employing over 4 million people, most of them women. Yet, squeezed by global competition, rising costs, ESG compliance, and shrinking lead times, the sector stands at a crossroads. The question now is simple, will we remain a volume-based manufacturing hub, or evolve into a smart, high-value, digitally-driven production ecosystem?
As the world's second-largest apparel exporter, the RMG industry contributes 10.35% to the national GDP and generates nearly USD 47 billion in annual exports, employing over 4 million people, most of them women. Yet, squeezed by global competition, rising costs, ESG compliance, and shrinking lead times, the sector stands at a crossroads. The question now is simple, will we remain a volume-based manufacturing hub, or evolve into a smart, high-value, digitally-driven production ecosystem?
The answer lies in one critical enabler: 5G-powered digital infrastructure.
1. Why Connectivity Matters for RMG
Inside most factories today, machines operate in isolation, supply chains remain partially manual, and quality checks rely heavily on human inspection. Poor indoor network connectivity means systems cannot "talk" to one another in real time. This is where 5G steps in, not as faster internet, but as the backbone of Industry 4.0.
Bangladesh RMG Sector: The Facts
• The RMG industry contributes around 10.35% of Bangladesh's GDP in FY2022 23.
• Total RMG export earnings in FY23 were about US$46.99 billion.
• The sector employs over 4 million people (majority women).
• RMGS account for more than 80% of Bangladesh's export revenue.
• Growth rates remain positive, though head winds exist (global slowdown, raw-material dependency).
hese numbers show tremendous scale and importance: the RMG sector is not just a manufacturing cluster, but a national export and employment engine. At the same time, the size implies major challenges that digital infrastructure could help resolve.
| "The future of Bangladesh's RMG industry will not be defined by cheaper labour, but by smarter connectivity." |
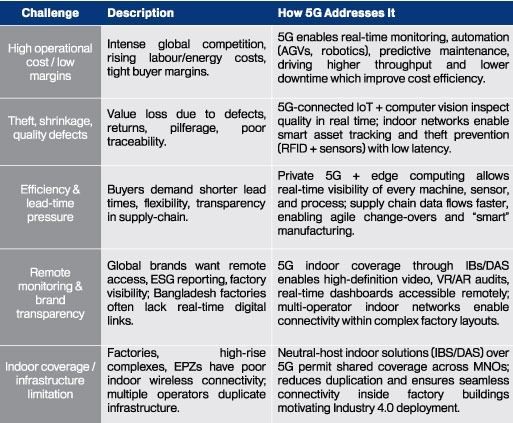
2. Key Challenges in the Garment Industry & How 5G Helps
Below are major pain points faced by the sector in Bangladesh, and how 5G enabled solutions can address them.
3. How 5G Transforms the Garment Sector: Use Cases
Here are more specific use cases in the RMG environment enabled by 5G:
• Real Time Quality Control: High speed, low latency 5G links cameras and Al systems on sewing lines to detect stitching errors or fabric flaws as they occur, reducing returns and improving brand reputation.
• Predictive Maintenance & loT: Dyeing machines, boilers, compressors fitted with sensors transmit data over 5G to edge/cloud platforms; anomalies flagged ahead of failure, avoiding costly downtime.
• Digital Twin & Smart Factory Floor: The factory floor is replicated virtually; simulations run in real time to optimise machine layout, material flow, worker deployment, energy consumption. With 5G ensuring throughput and reliability, decisions can be faster.
• Smart Logistics / AGVS Inside Factory: Autonomous guided vehicles moving materials rely on reliable indoor wireless connectivity; 5G private campus networks support their seamless operation and coordination.
• Worker Safety & ESG Compliance: Smart wearables, helmets, real time video analytics track worker movement, heat exposure, overcrowding, compliance with buyer standards. 5G enables high definition video feeds, sensor networks, real time alerts.
• Remote Collaboration & Global Buyers: Brands and inspectors across the world can join virtual walkthroughs, AR guided inspections, digital twin overlays, enabled by high bandwidth 5G connectivity inside Bangladesh factories, improving buyer confidence and reducing onsite visits overhead.

4. Case Study: 5G Smart Textile Workshop in China (Xinfengming Group)
One of the earliest and most cited examples of 5G in textile manufacturing is the Xinfengming Group's smart filament workshop in China. Xinfengming, a major chemical fiber producer, partnered with China Mobile and ZTE to build the world's first 5G-enabled textile workshop. This project was recognized in the GSMA's "5G Use Cases for Verticals" white paper as a breakthrough in the industry.
A 5G-connected inspection robot equipped with Al vision cameras patrols a textile production line. Such robots perform 24/7 quality checks, leveraging 5G to transmit data instantly for analysis.
Crucially, Xinfengming added machine vision and Al-powered quality control as part of the 5G upgrade. Automated inspection units now use 5G to send ultra-high resolution images of fibers and fabrics to Al systems that detect defects or irregularities in real time This has improved the consistency and "excellence rate❞ of products, while eliminating many manual check.
Key lessons:
• The combination of 5G+Al+loT yields measurable improvements in quality, throughput and export competitiveness.
• Shared/connected infrastructure (e.g., sensors, IGVS) across a manufacturing site can be made viable with 5G private networks.
• The gains are especially seen where legacy manufacturing was high volume but low digitisation; applying 5G upgrades the value chain.
Bangladesh's RMG sector can adopt similar principles, albeit scaled and adapted to the local context.

5. Conclusion: The Connectivity Dividend
The future of Bangladesh's RMG sector will not be decided by cheaper labor but by smarter connectivity. 5G is not an optional upgrade, it is a strategic necessity to retain global competitiveness, meet ESG demands, and unlock higher value manufacturing.
If we can connect every factory, every machine, and every worker to a real-time digital network, we will not only strengthen our export standing, but also empower millions of workers, enhance transparency for global brands, and position Bangladesh as a leader in digital manufacturing.
The success of Smart Bangladesh will be measured not by the number of mobile users but by how our factories become smarter, safer, and more sustainable.






